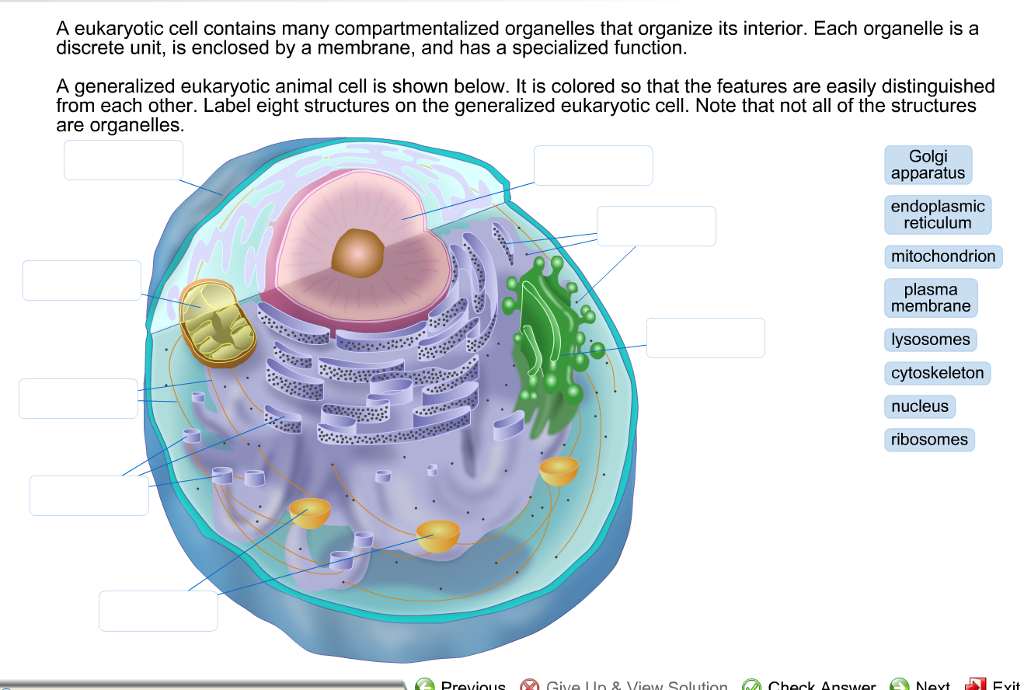
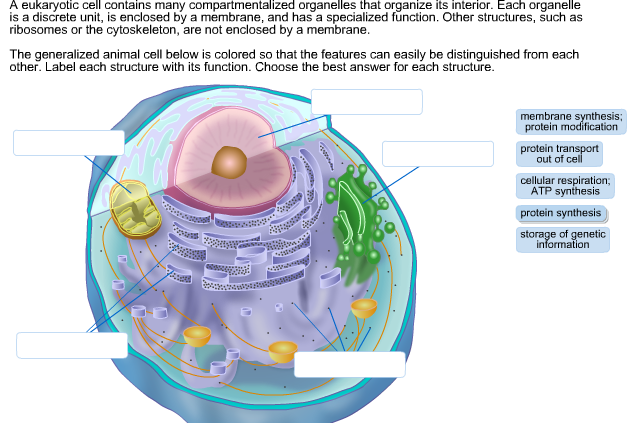
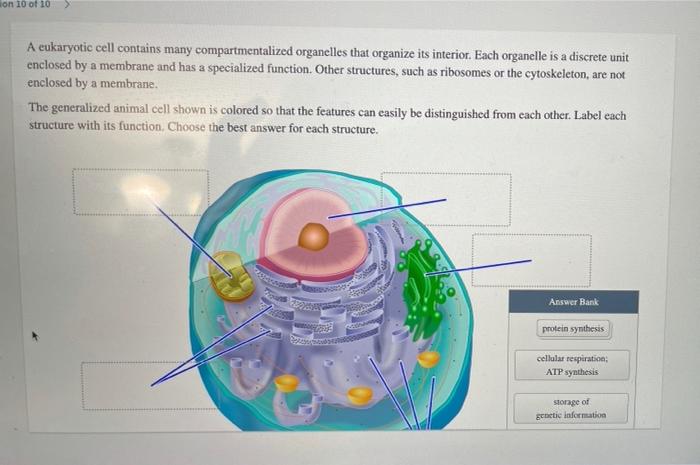
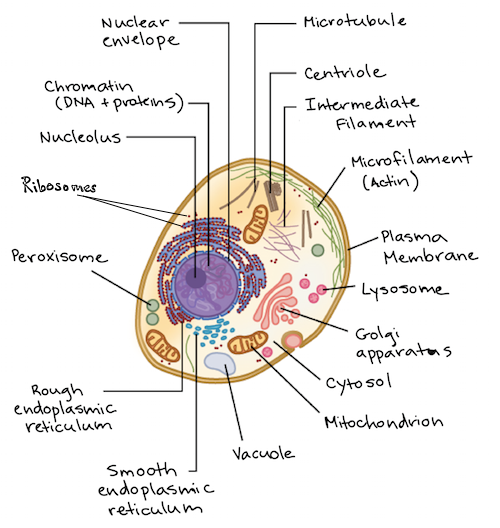
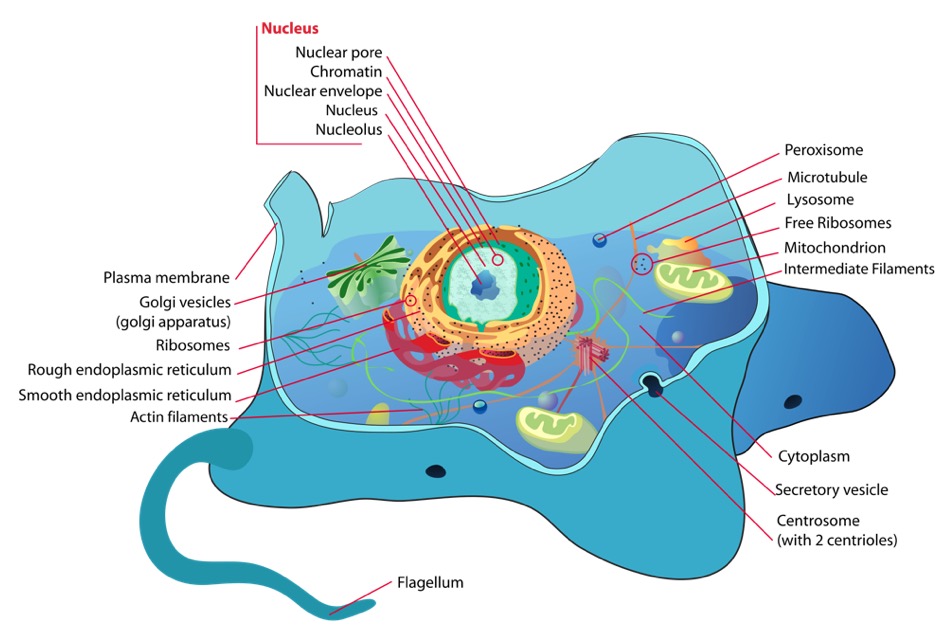
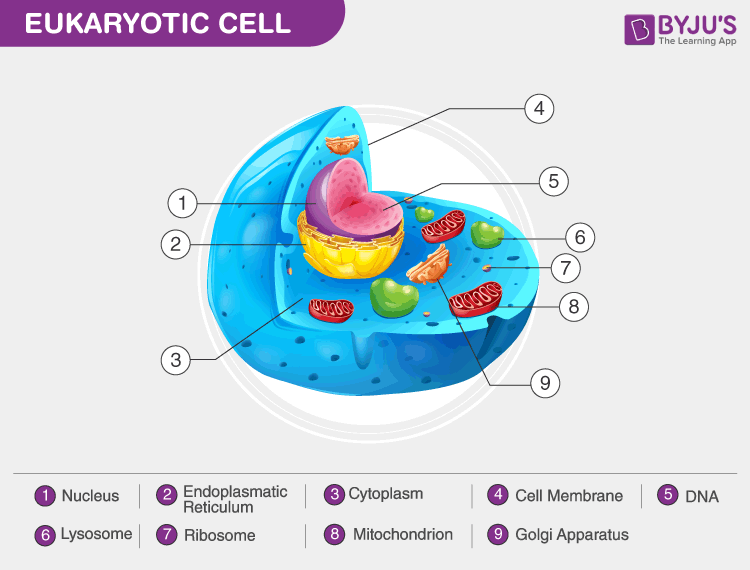
40 identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell.
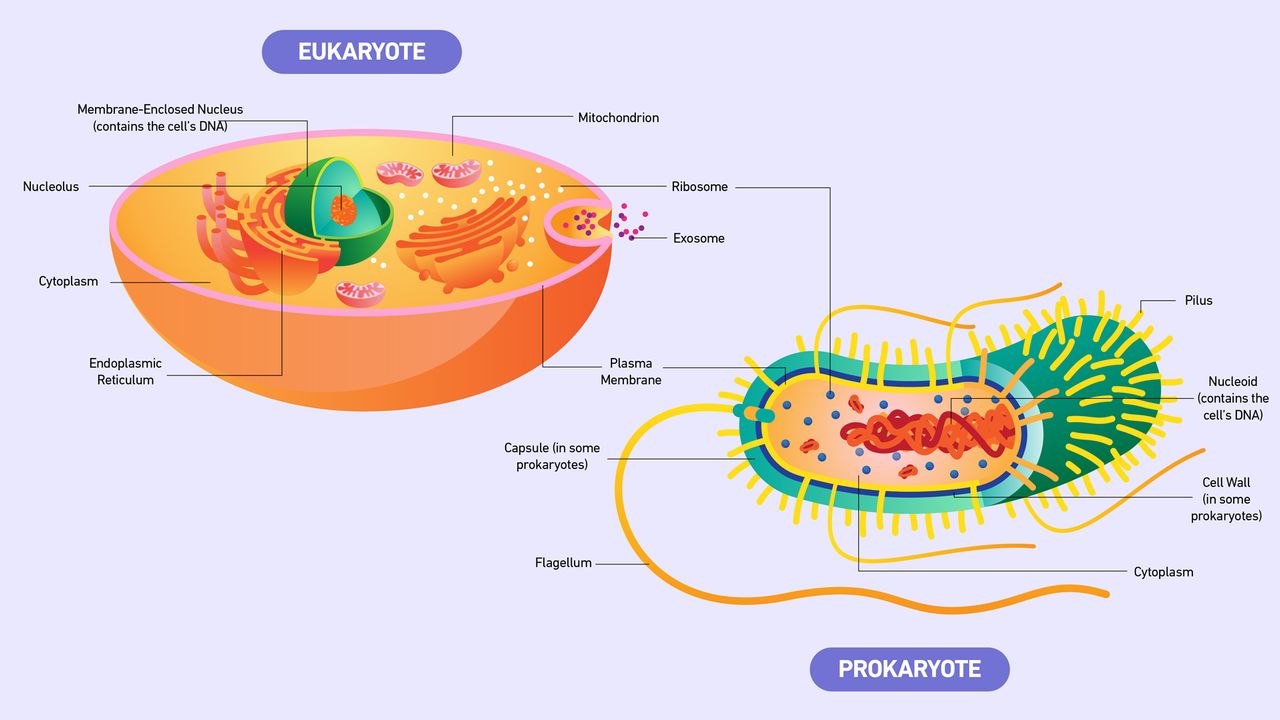
Eukaryotic Cell: Definition, Structure & Function (with ... - Sciencing Eukaryotic cells include animal cells - including human cells - plant cells, fungal cells and algae. Eukaryotic cells are characterized by a membrane-bound nucleus. That's distinct from prokaryotic cells, which have a nucleoid - a region that's dense with cellular DNA - but don't actually have a separate membrane-bound compartment like the nucleus. PDF Eukaryotic Cell Structure - Bellarmine University and eukaryotic cells 1. Create a Venn diagram or concept map that clearly distinguishes bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic cells in terms of their genome organization, organelles, cell envelopes, ribosome size and component molecules, and cytoskeleton. 2. Determine the type of microbe when given a description of a newly discovered microbe. 56
Eukaryotic Cell Parts, Functions & Diagram - Science Prof Online Flagella (singular flagellum), which are longer than cilia, aid in cell movement. Cilia (singular cilium), which are able to beat together in a coordinated manner, can also help direct materials around the outside of the cell. Sperm cells have a flagellum to help them reach the eggs for fertilization. See all related teaching materials on the

Identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell.
identify and label each part of the eukaryotic cell - Brainly.com Major parts of the eukaryotic animal cell are the nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, Golgi, ER, etc. What are animal cells? Animal cells are eukaryotes that lack cell walls but have almost the same components as plant cells. The cytoplasm is the component of the cell where all the organelle lies. How To Label A Plant Cell - Realonomics Each plant cell will have a cell wall cell membrane a nucleus smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus ribosomes plastids mitochondria vacuoles and various vesicles like peroxisomes.. What is cell Labelling? The visualization of cells and cellular structures as well as the tracking and modulation of nucleic acid and proteins in living cells is mandatory to identifiy map and ... Solved Can you identify the cellular structures and their - Chegg Part A Drag the organelle labels to the appropriate pink targets. Then identify the function of each organelle on the blue target below it. Resat Help Golg plasma Request Answer rovide Feedback Next > Question: Can you identify the cellular structures and their functions in this diagram of a eukaryotic cell? ?
Identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell.. Cells | Biology I Laboratory Manual - Lumen Learning identify whether a plant cell is a prokaryotic cell or a eukaryotic cell; identify whether a bacterial cell is a prokaryotic cell or a eukaryotic cell; ... Draw three representative cells, each about 2 cm in diameter. Label one cell with structures listed above. ... Label the cell parts you can distinguish. Label Eukaryotic Cell Flashcards | Quizlet Start studying Label Eukaryotic Cell. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Eukaryotic Cell Labeling Worksheet | Time for Worthing How enzymes for cell labeling the part of fatty acids and are the cell, passive transport ... Identify And Label Each Part Of This Eukaryotic. The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf Phases of the Cell Cycle. A typical eukaryotic cell cycle is illustrated by human cells in culture, which divide approximately every 24 hours. As viewed in the microscope, the cell cycle is divided into two basic parts: mitosis and interphase.Mitosis (nuclear division) is the most dramatic stage of the cell cycle, corresponding to the separation of daughter chromosomes and usually ending with ...
Answered: Label which parts of the cell… | bartleby Solution for Label which parts of the cell cytoplasm, nucleus, ETC. were stained with Harris Hematoxylin, EA-50, and OG-6 in your cheek lining. STAINED CHEEK… Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells - Course Hero The cytoskeleton is a network of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules found throughout the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. In these fluorescently labeled animal cells, the microtubules are green, the actin microfilaments are red, the nucleus is blue, and keratin (a type of intermediate filament) is yellow. PDF Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells - Grosse Pointe Public Schools Label each of these three organelles on the plant cell diagram in Model 3. 21. Individually, in one grammatically correct sentence, describe why it is necessary for plants to have chloroplasts. 22. As a group, reach a consensus on the answer to Question 21. Record the answer below. 23. The central vacuole stores water. Anatomy and Physiology: Parts of a Human Cell - Visible Body You, dear reader, are a eukaryotic being. You are made up of trillions of eukaryotic cells, of which there are over 200 different types. Each eukaryotic cell type specializes to perform certain functions. Bone cells, for example, form and regenerate bones. Ever fracture a bone? Within days, cells called fibroblasts begin to lay down bone matrix.
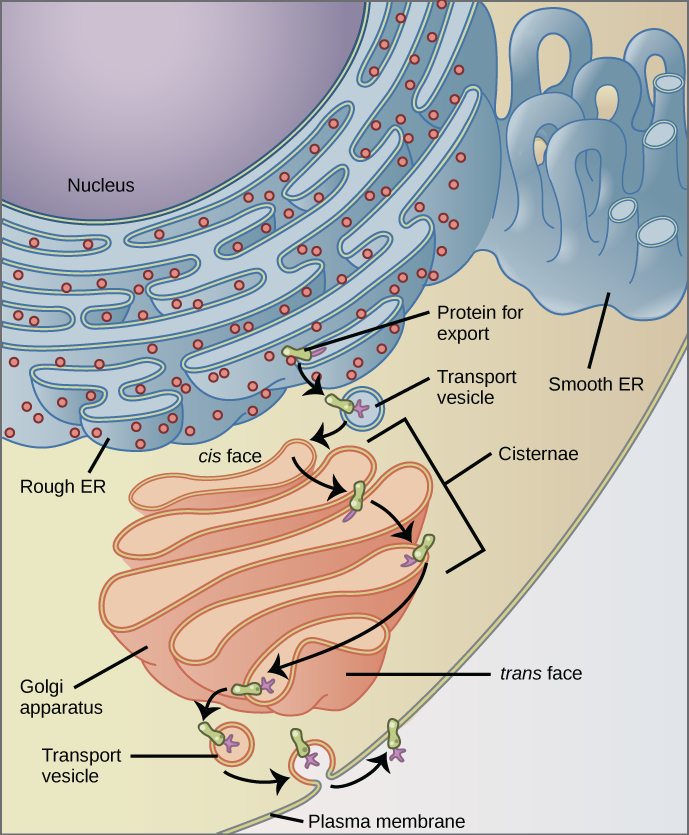
Eukaryotic Cells - Visible Body 1. Plant and animal cells are eukaryotic, meaning that they have nuclei. Eukaryotic cells are found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists. They generally have a nucleus—an organelle surrounded by a membrane called the nuclear envelope—where DNA is stored.There are a few exceptions to this generalization, such as human red blood cells, which don't have a nucleus when mature. Eukaryotic Cells | Biology I - Lumen Learning The endomembrane system ( endo = within) is a group of membranes and organelles (Figure 4) in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, and vesicles, the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, which we will cover shortly. Eukaryotic Cell Parts, Functions & Diagram - P3 - Science Prof Online Cytoplasm includes both the liquid (called cytosol) and the suspended organelles. Cytoskeleton: Composed of microtubules, intermediate filaments and microfilaments, this network of fibers provides an inner framework for the cell. The cytoskeleton supports the cells structure, anchors and helps transport organelles, and aids in cell division. Eukaryotic Cell - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary A eukaryotic cell contains membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus, mitochondria, and an endoplasmic reticulum. Organisms based on the eukaryotic cell include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals. These organisms are grouped into the biological domain Eukaryota.
Name - biologywithsteiner Label the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell. Cell membrane. Cytoplasm prokaryotic cell. ОИ. JAZ. 2. Explain why you labeled each diagram as you did.
3.3 Eukaryotic Cells - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition The endomembrane system ( endo = within) is a group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus, which we will cover shortly.
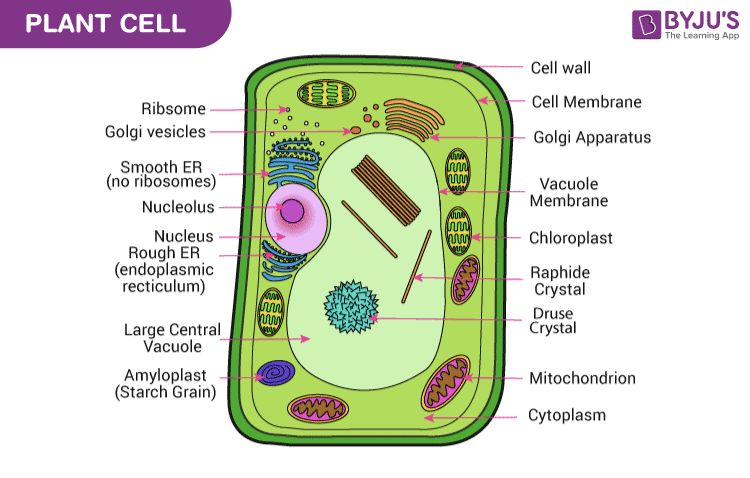
Eukaryotic Cells- Definition, Characteristics, Structure, & Examples The eukaryotic cell structure comprises the following: Plasma Membrane The plasma membrane separates the cell from the outside environment. It comprises specific embedded proteins, which help in the exchange of substances in and out of the cell. Cell Wall A cell wall is a rigid structure present outside the plant cell.
Eukaryotic Cell: Structure, Characteristics & Diagram - Embibe A eukaryotic cell is an advanced type of cell that has a well-defined nucleus and multiple membrane-bound organelles. DNA is the genetic material of the eukaryotic cell. The nucleus is surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane. Eukaryotic cells have mitochondria for cellular respiration.
Learn the parts of a cell with diagrams and cell quizzes - Kenhub The first is the cell nucleus, which houses DNA in the form of chromosomes. The second is the cytoplasm, a thick solution mainly comprised of water, salts, and proteins. The parts of a eukaryotic cell responsible for maintaining cell homeostasis, known as organelles, are located within the cytoplasm.
PDF 1 SECTION 2 Eukaryotic Cells - LAB RATKOS A eukaryotic cell has many parts that help the cell stay alive. CELL WALL All plant cells have a cell wall. The cell wall is a stiff structure that supports the cell and surrounds the cell membrane. The cell wall of a plant cell is made of a type of sugar called cellulose. Fungi (singular fungus), such as yeasts and mushrooms, also have cell walls.
Organelles of Eukaryotic Cells - Windows to the Universe The "brains" of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA. Mitochondria. Make energy out of food. Ribosomes. Make protein. Golgi Apparatus. Make, process and package proteins. Lysosome. Contains digestive enzymes to help break food down.
Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram Plant cells are eukaryotic cells, that are found in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae which means they have a membrane-bound nucleus. They have a variety of membrane-bound cell organelles that perform various specific functions to maintain the normal functioning of the plant cell. Structure of Plant cell
identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell - Brainly.com answered Identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell Advertisement Answer 2 rawan12343 can you take a picture so I can help you identify it. Still stuck? Get 1-on-1 help from an expert tutor now. yes the nucleus would be your answer. Advertisement Answer 5.0 /5 5 jenniferlove131418 Answer: Label A nucleus Label B cytoplasm Label C
Eukaryotic Cell Labeling Diagram | Quizlet Eukaryotic Cell Labeling STUDY Learn Write Test PLAY Match + − Created by tasheia_floyd Terms in this set (20) Nuclear Envelope ... Nucleus ... Chromatin ... Nucleus ... Ribosomes ... Golgi Apparatus ... Lysosome ... Mitochondira ... Peroxisome ... Microvilli ... Microtubules ... Intermediate Filaments ... Microfilaments ... Cytoskeleton ...
Eukaryotic Cells - Definition, Parts, Examples, and Structure Eukaryotic cells are defined as cells containing organized nucleus and organelles which are enveloped by membrane-bound organelles. Examples of eukaryotic cells are plants, animals, protists, fungi. Their genetic material is organized in chromosomes. Golgi apparatus, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Nucleus are parts of Eukaryotic Cells.
A Well-labelled Diagram Of Animal Cell With Explanation - BYJUS Diagram Of Animal Cell Animal cells are eukaryotic cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus. They are different from plant cells in that they do contain cell walls and chloroplast. The animal cell diagram is widely asked in Class 10 and 12 examinations and is beneficial to understand the structure and functions of an animal.
Solved Can you identify the cellular structures and their - Chegg Part A Drag the organelle labels to the appropriate pink targets. Then identify the function of each organelle on the blue target below it. Resat Help Golg plasma Request Answer rovide Feedback Next > Question: Can you identify the cellular structures and their functions in this diagram of a eukaryotic cell? ?
How To Label A Plant Cell - Realonomics Each plant cell will have a cell wall cell membrane a nucleus smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus ribosomes plastids mitochondria vacuoles and various vesicles like peroxisomes.. What is cell Labelling? The visualization of cells and cellular structures as well as the tracking and modulation of nucleic acid and proteins in living cells is mandatory to identifiy map and ...
identify and label each part of the eukaryotic cell - Brainly.com Major parts of the eukaryotic animal cell are the nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, Golgi, ER, etc. What are animal cells? Animal cells are eukaryotes that lack cell walls but have almost the same components as plant cells. The cytoplasm is the component of the cell where all the organelle lies.























Post a Comment for "40 identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell."