39 nodes and antinodes
Nodes and Antinodes in A Tuning Fork / Physics Made Simple / Revise ... NODES AND ANTINODES IN A TUNING FORK , PHYSICS MADE SIMPLE , REVISE PHYSICS FOR NEET JEE IN #Shorts #JEE #targetneet2021 #neetrevision #EAMCET #KCET #Un... en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Node_(physics)Node (physics) - Wikipedia Many of these quantum waves have nodes and antinodes as well. The number and position of these nodes and antinodes give rise to many of the properties of an atom or covalent bond. Atomic orbitals are classified according to the number of radial and angular nodes, while molecular orbitals are classified according to bonding character. Molecular ...
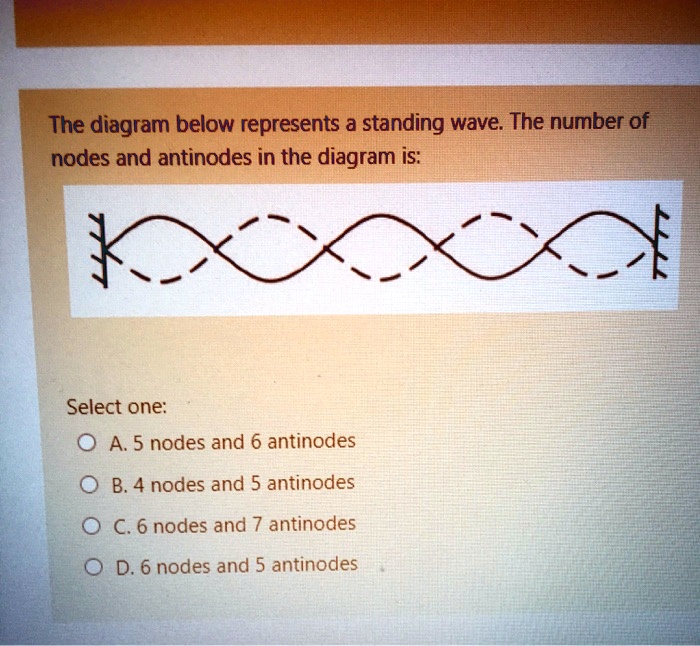
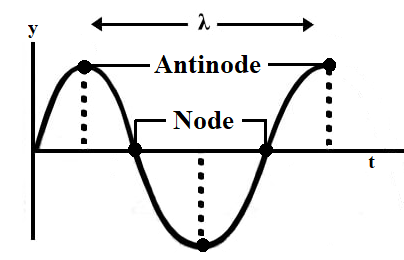
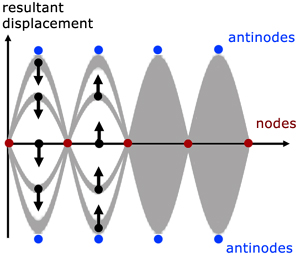
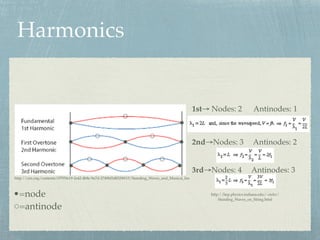
Formula for nodes and antinodes? This pattern with three nodes and two antinodes is referred to as the second harmonic and is depicted in the animation shown below. What are nodes and antinodes physics? A node is where the amplitude of the wave is zero. Antinodes are where the amplitude (positive of negative) is a maximum, halfway between two adjacent nodes.

Nodes and antinodes
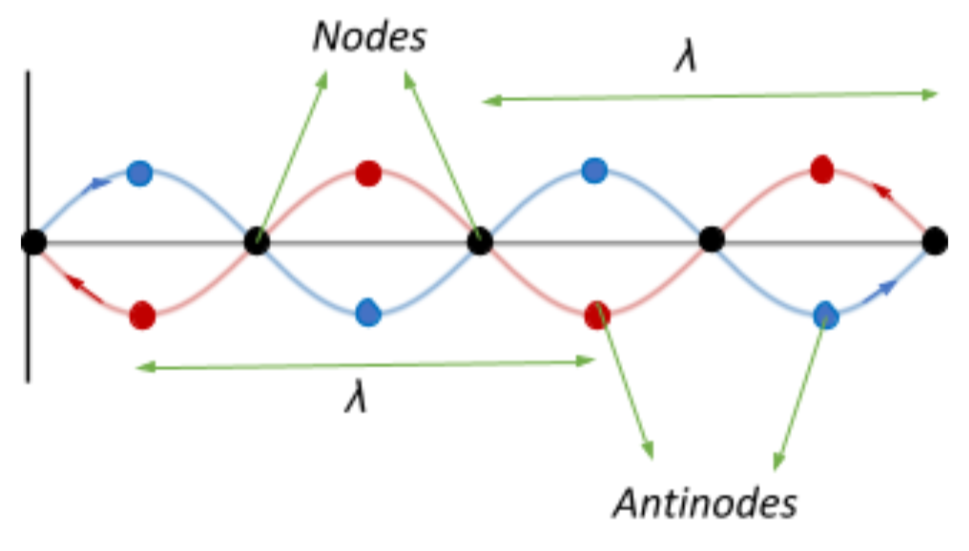
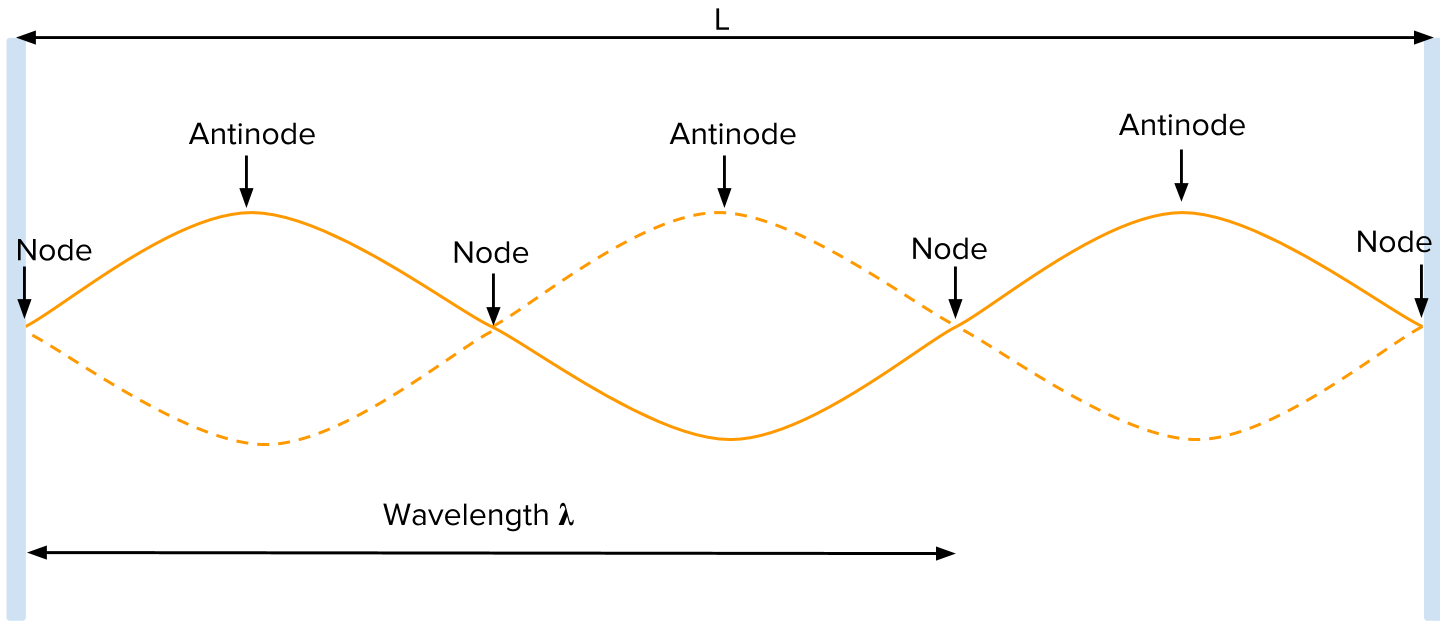
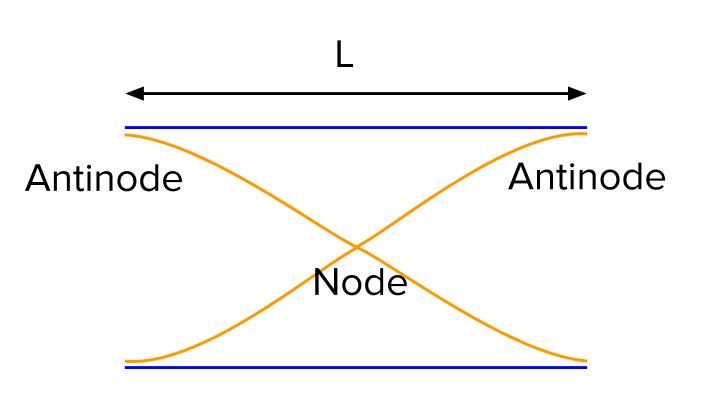
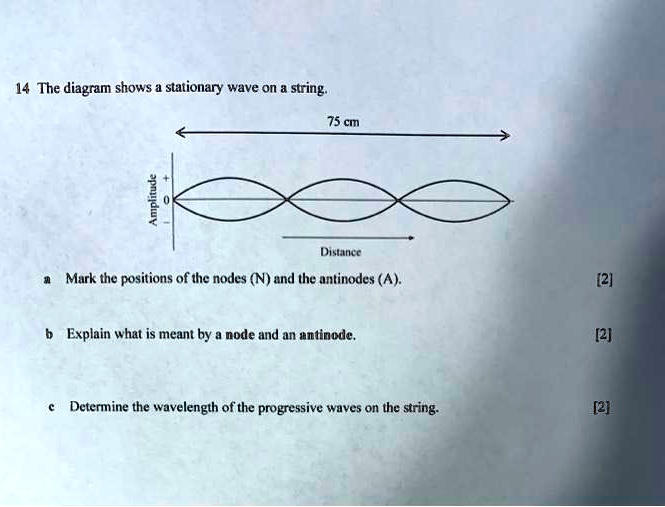
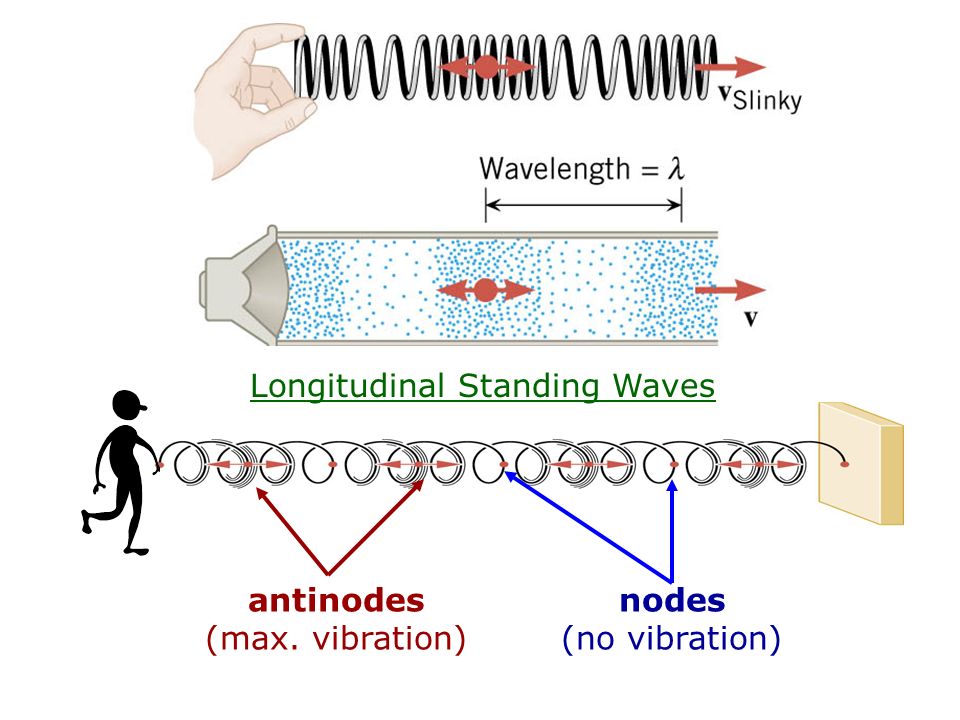
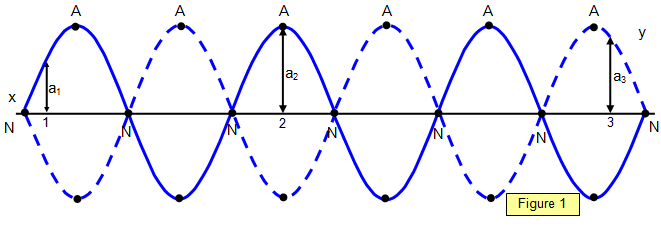
Topic 4: Waves – IB Physics Nodes and antinodes; Positions along the wave which are fixed are called nodes (minimum) and those with the largest displacement are called antinodes (maximum). For standing waves, the distance between adjacent nodes = the distance between adjacent antinodes = λ/2. FYI. Difference between standing waves and travelling waves Physics Tutorial: Nodes and Anti-nodes - Physics Classroom Nodes and antinodes should not be confused with crests and troughs. When the motion of a traveling wave is discussed, it is customary to refer to a point of large maximum displacement as a crest and a point of large negative displacement as a trough.These represent points of the disturbance that travel from one location to another through the medium. . An antinode on the … EOF
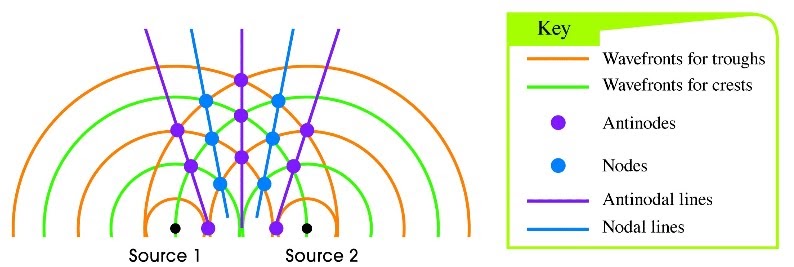
Nodes and antinodes. What is a node What is an antinode class 11 physics CBSE - Vedantu The positioning of the nodes and antinodes during a standing wave pattern are often explained by focusing on the interference of the 2 waves. The nodes are produced at locations where destructive interference occurs. as an example, nodes form at locations where a crest of 1 wave meets a trough of a second wave; or a half-crest of 1 wave meets a ... Nodes and Antinodes Flashcards | Quizlet These are waves that have moving points and non-moving points Node point in a standing wave that has the LEAST displacement (maintains zero displacement) antinode a point in the standing wave, halfway between two nodes, at which the MOSTdisplacement occurs adding to amplitude What is Cymatics? The Art and Science of Visible Sound Explained This creates nodes and antinodes (behaviour of the waves at the points of minimum and maximum vibrations, in this case, points of amplified peaks and troughs) Nodes: Points which are stationary and with zero amplitude. At nodes, two waves travel in exactly same amplitude and out of phrase offset with each other. Antinodes: Points at maximum ... Nodes and Antinodes - Spherical Aberration - Bedford Astronomy Club There are two nodes at the bridge and fret, and a single antinode at the center. This situation is called a standing wave. Of course, the presence of the two nodes at the edges of the string is hardly a surprise. These positions are mechanically constrained and can hardly be expected to move much. 4.4. Nodes and Antinodes. Fig. 4-11.
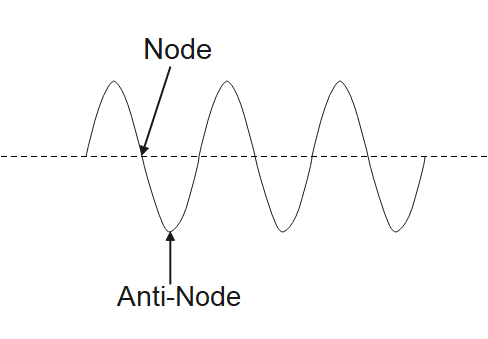
Node (physics) - Wikipedia A node is a point along a standing wave where the wave has minimum amplitude.For instance, in a vibrating guitar string, the ends of the string are nodes. By changing the position of the end node through frets, the guitarist changes the effective length of the vibrating string and thereby the note played. The opposite of a node is an anti-node, a point where the amplitude of the … › Nodes-and-Anti-nodesPhysics Tutorial: Nodes and Anti-nodes - Physics Classroom The nodes and antinodes are labeled on the diagram. When a standing wave pattern is established in a medium, the nodes and the antinodes are always located at the same position along the medium; they are standing still. It is this characteristic that has earned the pattern the name standing wav e. Flickr Physics Photo Vibrating structure gyroscope - Wikipedia Standing waves are elliptically-shaped oscillations with four antinodes and four nodes located circumferentially along the rim. The angle between two adjacent antinode – nodes is 45 degrees. One of the elliptical resonant modes is excited to a prescribed amplitude. When the device rotates about its sensitive axis (along its inner stem), the ... Node and antinode | SpringerLink Nodes are points at which the displacement of oscillating water surface is always zero, while the amplitude of oscillations in antinodes is maximum. Both features result from the superposition of two or more progressive waves propagating in opposite directions in a body of water. Quasinodes and antinodes appear in partially reflected waves.
Chladni Plates | Harvard Natural Sciences Lecture Demonstrations Accumulation of sand at nodes of vibrating plate reveals resonance patterns. What It Shows A Chladni plate consists of a flat sheet of metal, usually circular or square, mounted on a central stalk to a sturdy base. When the plate is oscillating in a particular mode of vibration, the nodes and antinodes that are set up form complex but symmetrical patterns over its surface. The … sciencedemonstrations.fas.harvard.eduChladni Plates | Harvard Natural Sciences Lecture Demonstrations Accumulation of sand at nodes of vibrating plate reveals resonance patterns. What It Shows A Chladni plate consists of a flat sheet of metal, usually circular or square, mounted on a central stalk to a sturdy base. When the plate is oscillating in a particular mode of vibration, the nodes and antinodes that are set up form complex but symmetrical patterns over its surface. The positions of ... journeyofcuriosity.net › pages › what-is-cymaticsWhat is Cymatics? The Art and Science of Visible Sound ... This creates nodes and antinodes (behaviour of the waves at the points of minimum and maximum vibrations, in this case, points of amplified peaks and troughs) Nodes: Points which are stationary and with zero amplitude. At nodes, two waves travel in exactly same amplitude and out of phrase offset with each other. Antinodes: Points at maximum ... What is node and antinode in waves? - Quora A node is where the amplitude of the wave is zero. Antinodes are where the amplitude (positive of negative) is a maximum, halfway between two adjacent nodes. In a traveling wave, both move with the propagation velocity of the wave. In a standing wave (composed of two traveling waves propagating in opposite directions) they are stationary.
Nodes and Antinodes (Strings and Pipes) - YouTube and Antinodes on strings and in pipes.
Clapotis - Wikipedia In hydrodynamics, a clapotis (from French for "lapping of water") is a non-breaking standing wave pattern, caused for example, by the reflection of a traveling surface wave train from a near vertical shoreline like a breakwater, seawall or steep cliff. The resulting clapotic wave does not travel horizontally, but has a fixed pattern of nodes and antinodes.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Standing_waveStanding wave - Wikipedia Standing waves can be mechanically induced into a solid medium using resonance. One easy to understand example is two people shaking either end of a jump rope. If they shake in sync, the rope will form a regular pattern with nodes and antinodes and appear to be stationary, hence the name standing wave.
Resonances of open air columns - GSU Air Column Resonance. The resonant frequencies of air columns depend upon the speed of sound in air as well as the length and geometry of the air column. Longitudinal pressure waves reflect from either closed or open ends to set up standing wave patterns. Important in the visualization of these standing waves is the location of the nodes and antinodes of pressure …
Antinodes - definition of antinodes by The Free Dictionary antinode ( ˈæntɪˌnəʊd) n (General Physics) physics a point at which the amplitude of one of the two kinds of displacement in a standing wave has maximum value. Generally the other kind of displacement has its minimum value at this point. See also standing wave Compare node ˌantiˈnodal adj
What Is The Difference Between A Node And Antinode? For example, the two ends of a string vibrating is the node. At the point of the node, the particle of the standing wave does not vibrate. The opposite of the node is anti-node, so anti-node is a point where the amplitude of the standing wave is maximum.. What is node and antinode in chemistry?
What is node and anti node? - UrbanPro Answer Atmanand Prasad Friendly & Energetic Teacher 31/01/2015 Node (physics) A node is a point along a standing wave where the wave has minimum amplitude. For instance, in a vibrating guitar string, the ends of the string are nodes. Anti node-the position of maximum displacement in a standing wave system. 2 Comments Raj Kumar Tutor 31/01/2015
Define antinodes and nodes. | Physics Questions - Toppr Ask Define antinodes and nodes. Medium Solution Verified by Toppr 1. Some medium particles ( A 1,A 2,A 2,A 4 and A 5) always vibrate with the maximum amplitude on both the sides of the mean position. They are called antinode. Velocity (dy/dt) of particles at antinodes is, maximum and pressure or change in density is zero. [∵ dxdy=0]
Standing wave - Wikipedia As an example of the second type, a standing wave in a transmission line is a wave in which the distribution of current, voltage, or field strength is formed by the superposition of two waves of the same frequency propagating in opposite directions. The effect is a series of nodes (zero displacement) and anti-nodes (maximum displacement) at fixed points along the transmission …
ibphysics.org › topic4Topic 4: Waves – IB Physics Nodes and antinodes; Positions along the wave which are fixed are called nodes (minimum) and those with the largest displacement are called antinodes (maximum). For standing waves, the distance between adjacent nodes = the distance between adjacent antinodes = λ/2. FYI. Difference between standing waves and travelling waves
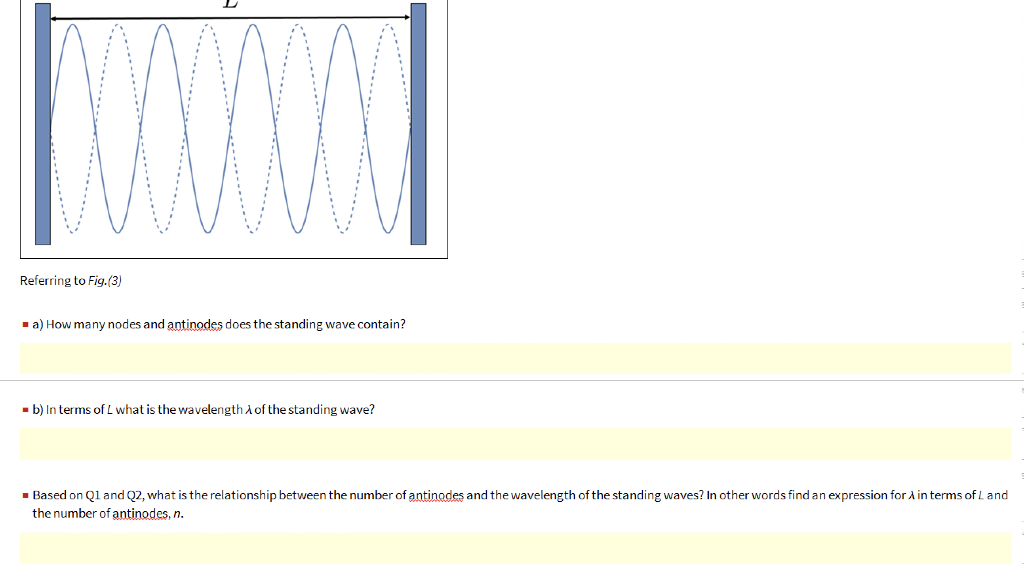
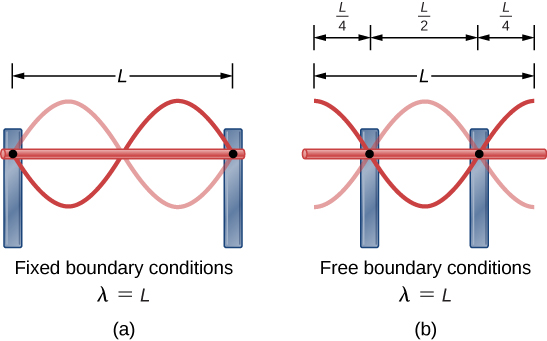
Lab 1: Standing Waves - University of Tennessee Standing wave patterns are always characterized by an alternating pattern of nodes and antinodes. Transverse waves on a string. Standing waves of many different wavelengths can be produced on a string with two fixed ends, as long as an integral number of half wavelengths fits into the length of the string. For a standing wave on a string of ...
Nodes and Antinodes Lab - Docest 3.To demonstrate the true nature of a node and an antinode, place a note card in between two adjacent coils of the spring at both a nodal and an antinodal position. Silence occurs when placed at the nodal position and the sound of chattering teeth is heard when placed at the antinodal position.
Nodes and Anti-nodes - Mechanical Engineering What are Nodes and Antinodes? One characteristic of every standing wave pattern is that there are points along the medium that appear to be standing still. These points, sometimes described as points of no displacement, are referred to as nodes. There are other points along the medium that undergo vibrations between a large positive and large ...
Pressure Nodes and Antinodes - Physics Lens According to Young & Geller (2007), College Physics 8th Edition, Pearson Education Inc. (pg 385), microphones and similar devices usually sense pressure variations and not displacements. In other words, the position within a stationary sound wave at which the loudest sound is picked up is at the displacement nodes which are the pressure antinodes.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Vibrating_structure_gyroscopeVibrating structure gyroscope - Wikipedia The resonator is operated in its second-order resonant mode. The Q-factor is usually about 20,000; that pre-determines its noise and angular random walks. Standing waves are elliptically-shaped oscillations with four antinodes and four nodes located circumferentially along the rim. The angle between two adjacent antinode – nodes is 45 degrees.
What is a node? What is an antinode? - Chemistry QA - BYJU'S Anti node The opposite of a node is an antinode, a point where the amplitude of the standing wave is a maximum. These occur midway between the nodes. At antinodes, the amplitude is maximum. In case of the standing wave amplitude is given as :- 2asinkx => 2asinkx = maximum. This value is maximum only when sinkx=1.
EOF
Physics Tutorial: Nodes and Anti-nodes - Physics Classroom Nodes and antinodes should not be confused with crests and troughs. When the motion of a traveling wave is discussed, it is customary to refer to a point of large maximum displacement as a crest and a point of large negative displacement as a trough.These represent points of the disturbance that travel from one location to another through the medium. . An antinode on the …
Topic 4: Waves – IB Physics Nodes and antinodes; Positions along the wave which are fixed are called nodes (minimum) and those with the largest displacement are called antinodes (maximum). For standing waves, the distance between adjacent nodes = the distance between adjacent antinodes = λ/2. FYI. Difference between standing waves and travelling waves




















Post a Comment for "39 nodes and antinodes"